Neurodevelopment
Neurodevelopment is the brain’s ability to develop the neurological pathways responsible for the normal functioning of the brain’s ability to learn, focus, develop memories and social skills, etc. Effectively, everything a human being does on a daily basis such as reading, writing, listening, watching, is contributing to neurodevelopment of the brain.

Neurodevelopment FAQ’s
What is Neurodevelopment?
The objective of neurodevelopment is to improve the learning process through training exercises, which identify and strengthen weak neurodevelopmental units. Deficits in the natural processes of neurodevelopment are typically characterized by disorders such as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), motor disorders such as tics, communication disorders, and intellectual developmental disorders. Neurodevelopmental methods can identify and improve deficits by analyzing the neuropathways associated with that specific deficit harnessing the power of neuroplasticity.
Stages of Neurodevelopment
The architecture of the adult brain is developed during the embryological formation of the nervous system. The first cellular processes that occur in the brain are neurogenesis, cell migration, cell differentiation, synaptogenesis, neuronal cell death, and synaptic rearrangement. The intricate interplay of these stages produces circuits that mediate a highly complex set of behaviors. These neural circuits continue to develop and are shaped by interactions between the brain and the environment during infant neurodevelopment.
Neurodevelopment Research Techniques
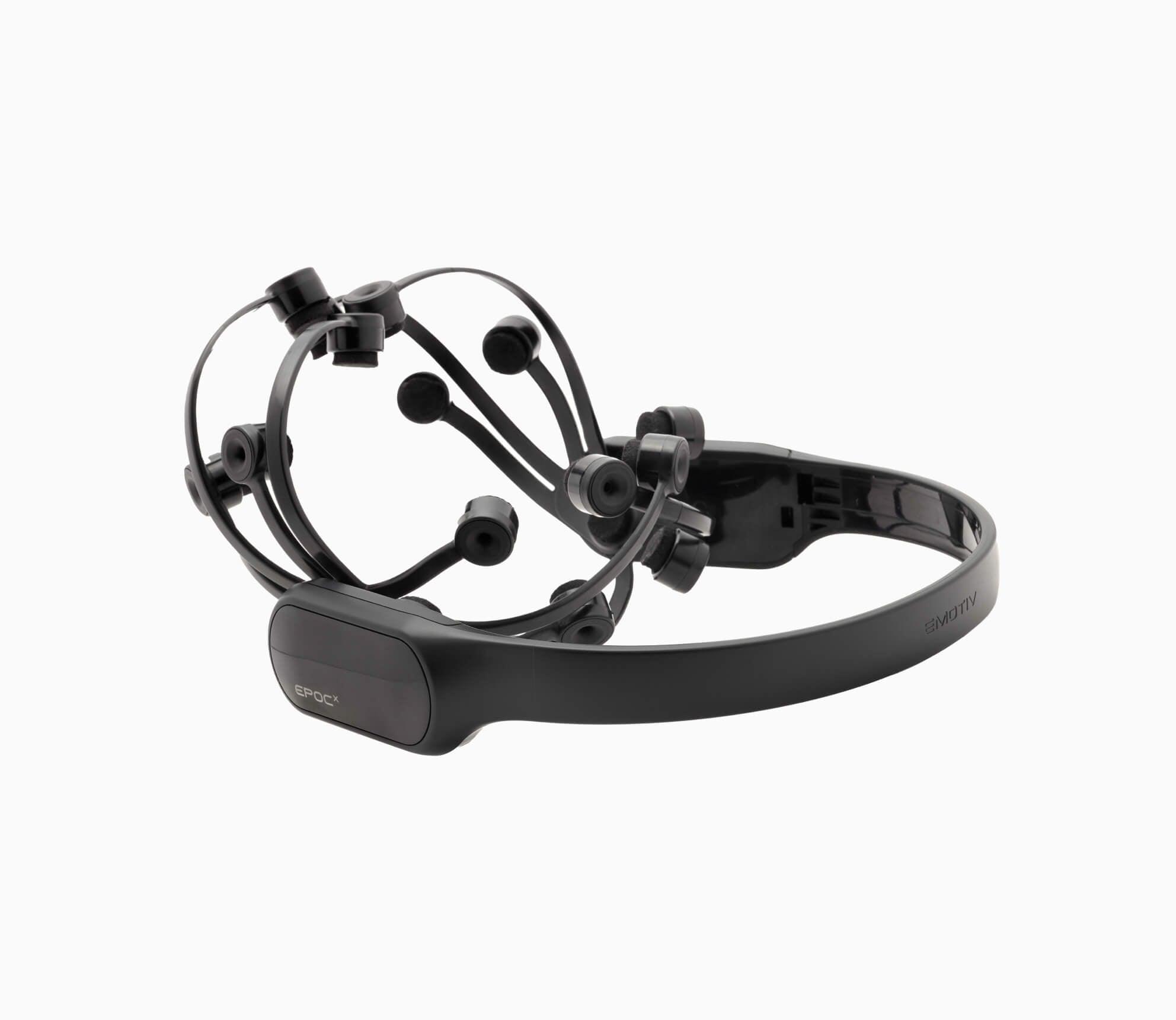
Neurodevelopmental research is the cross-disciplinary collaboration of scientists working towards a more thorough understanding of the origin, maintenance, prevention, and treatment of mental illness. Understanding the neurodevelopmental origins of mental illness is essential in defining the mechanism of action of a particular mental disorder, further facilitating the detection of covert disease processes and providing the opportunity to engage in an early-stage intervention. Using noninvasive spectral imaging through such methods as EEG monitoring, researchers can examine neuro-pathways and identify deficits in the natural processes of neurodevelopment.
Treatment facilities dedicated to neurodevelopment research offer individuals a range of neurotherapies to address various mental disorders. For example, the Neuro Development Center in Rhode Island focuses on tailoring intensive brain exercises to meet the needs conveyed by each individual’s EEG biofeedback.
What Causes Neurodevelopmental Disorders?
Neurodevelopmental disorders can be caused by any minor deviation from the highly intricate and precise development of the nervous system. Both external influences from the environment and genetic abnormalities can affect child neurodevelopment, impairing the growth of the brain and contributing to the development of a variety of mental disorders. Causes of neurodevelopmental disorders include physical trauma, immune dysfunction, infectious diseases, nutrition disorders, genetic disorders, metabolic disorders, and social deprivation.
Does EMOTIV Offer Neurodevelopment Research Tools?
EEG data can be a powerful tool for predicting mental disorders. Using computational algorithms with a variety of measures of signal complexity, scientists can analyze EEG data with high specificity to identify abnormal brain function. EMOTIV offers a dynamic array of hardware and software solutions for neurodevelopment research. Emotiv EEG headsets produce clean, robust signals, facilitating thorough, noninvasive neuroimaging with clinical accuracy. Researchers can analyze real-time bioinformatics or download datasets for further analysis. EMOTIV’s simple design and ease of use make EEG monitoring an accessible method for brain research.